Case File — Patterson–Gimlin Bigfoot Film (1967)

Overview
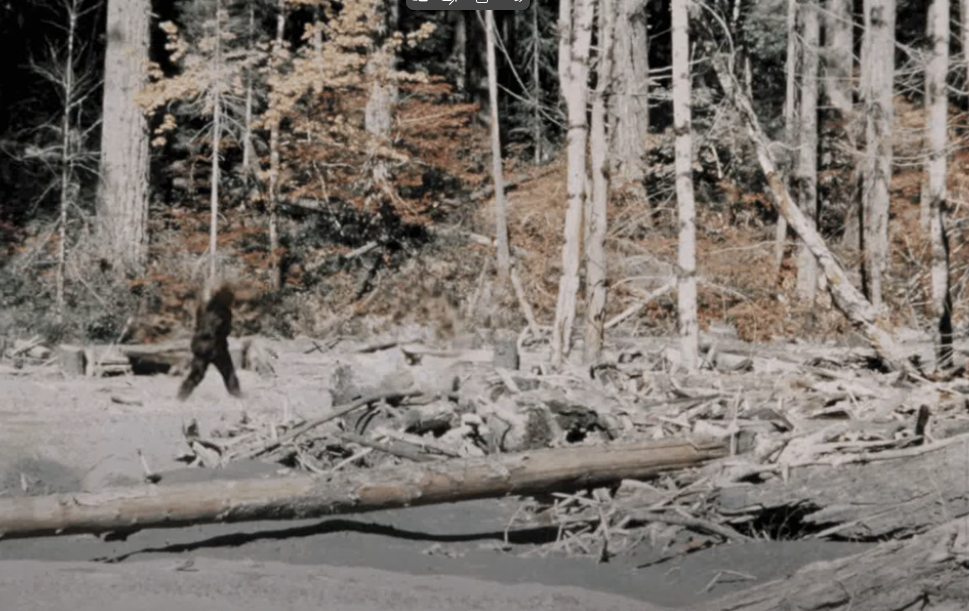
On October 20, 1967, Roger Patterson and Bob Gimlin filmed a walking, hair-covered figure at Bluff Creek, California. The 59 seconds of 16 mm footage became the most famous Bigfoot clip and a cultural icon. Supporters argue the gait and body proportions look non-human. Skeptics call it a man in a suit. The debate has never been resolved. opbWikipedia
Timeline
- Oct 20, 1967: Patterson and Gimlin record the footage at Bluff Creek during a horseback search. opbWikipedia
- 1967–1968: The film is shown to media and at scientific gatherings. Interest is high, but opinions split. Wikipedia
- 1998: Forensic examiner Jeff Glickman publishes an analysis, “Toward a Resolution of the Bigfoot Phenomenon.” Idaho State University
- 2002–2004: Bob Heironimus claims he wore a gorilla suit for the film. Skeptical Inquirer publishes a hoax account. cdn.centerforinquiry.org
- 2013: Bill Munns and Jeff Meldrum publish a technical paper on image integrity in Relict Hominoid Inquiry. Idaho State University
- 2017–present: The film remains a touchstone in Bigfoot culture and media retrospectives. Frame 352 becomes the iconic still. opb
Primary sources
- Stabilized footage (YouTube embed). YouTube
- Unedited clip (Wikimedia Commons). Wikimedia Commons
- Glickman 1998 forensic analysis reference. Idaho State University
- Munns and Meldrum 2013 image integrity study. Idaho State University
- Skeptical Inquirer hoax write-up with Heironimus claims. cdn.centerforinquiry.org
- OPB backgrounder on the film’s history and cultural impact. opb
Claims and counterclaims
Claim: The subject shows non-human gait, shoulder breadth, and soft-tissue movement that would be hard to fake with 1967 costuming.
Counter: Effects artists and skeptics argue a suit is plausible. The film speed is uncertain, which affects gait analysis. Some experts have publicly called it a man in a suit, and a named individual has claimed to be the person in costume. Idaho State UniversityWikipediacdn.centerforinquiry.org
Claim: Technical analysis supports authenticity.
Counter: Analyses in favor rely on copies and indirect data. Skeptical treatments point to Patterson’s showmanship, money disputes, and the lack of chain-of-custody style documentation. Idaho State UniversityWikipedia
Credibility meter
Score each 1 to 5.
- Witnesses: 2
Two principals, few independent contemporaneous witnesses on scene. Wikipedia - Physical evidence: 1
No specimen or confirmed biological trace tied to the subject. - Documentation: 3
Film exists in multiple generations, but original-context metadata and camera settings are debated. Wikipedia - Expert review: 2–3
Technical arguments on both sides, no consensus. Idaho State Universitycdn.centerforinquiry.org
Overall: ~2.3 (contested, culturally important)
Red flags
- Camera frame rate and some filming details are uncertain, which changes gait math. Wikipedia
- A named individual claimed to have worn a suit, and a skeptical investigation documented that narrative. cdn.centerforinquiry.org
What we know
- The footage was filmed at Bluff Creek on Oct 20, 1967, and the still known as Frame 352 became an icon. opb
- The clip has been stabilized and re-digitized many times, improving viewability but not resolving the core dispute. YouTube
Unknowns
- Whether the subject is a living animal or a person in a costume.
- The exact frame rate used during filming, which affects stride and speed estimates. Wikipedia
Where to dig next
- Analyze first-generation copies and camera data to bound frame rate and stride. Idaho State University
- Compare modern suit-making capabilities in 1967 with the film’s visible surface dynamics using documented effects methods from that era.
- Map the film site geometry and lines of sight to refine size estimates from known objects in frame. opb
Receipts
- OPB: history and significance, Frame 352. opb
- Wikipedia summary with filming details and debate overview. Wikipedia
- Glickman 1998 reference in RHI brief. Idaho State University
- Munns and Meldrum 2013 image integrity paper. Idaho State University
- Skeptical Inquirer hoax account featuring Heironimus claims. cdn.centerforinquiry.org
- YouTube stabilized clip for embedding. YouTube
- Wikimedia Commons unedited clip. Wikimedia Commons